The technologies that set the course to the new quantum era
Quantum technologies are set to lead a revolution that will have a significant impact on industry and on everyday life.
Their disruptive nature opens the way to a new era in which the capabilities of information technologies increase exponentially in scope and efficiency. For this reason, the quantum era is identified with a new era of knowledge economy.
What are quantum technologies?
Quantum technologies are based on the principles of quantum physics, which studies matter and energy at its most fundamental level with the aim of discovering the properties and behaviors of the basic components of nature.
The quantum scenario opens up opportunities that were unforeseen until now. In general terms, there are two phenomena that feed these technologies to perform tasks more efficiently and to perform difficult or impossible calculations using classical technologies:
Quantum superposition
In which a particle can be in different states at the same time.
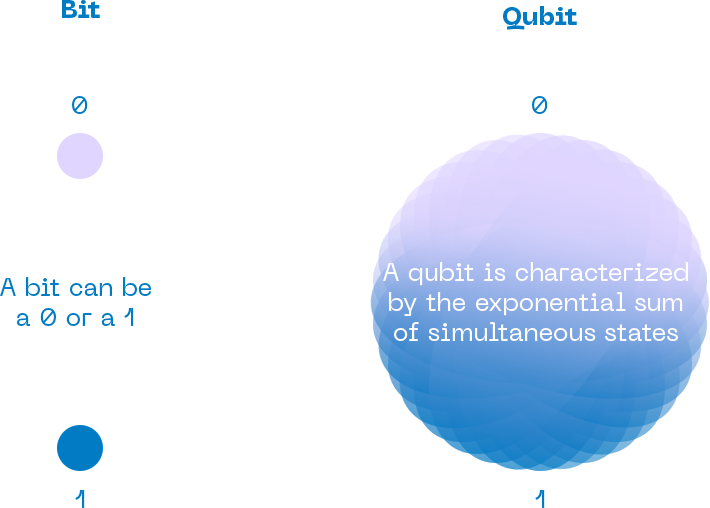
With more particles, the number of posibilities increases.
10 bits = 1 state of 10 bits each time
10 qubits = 1024 simultaneous states
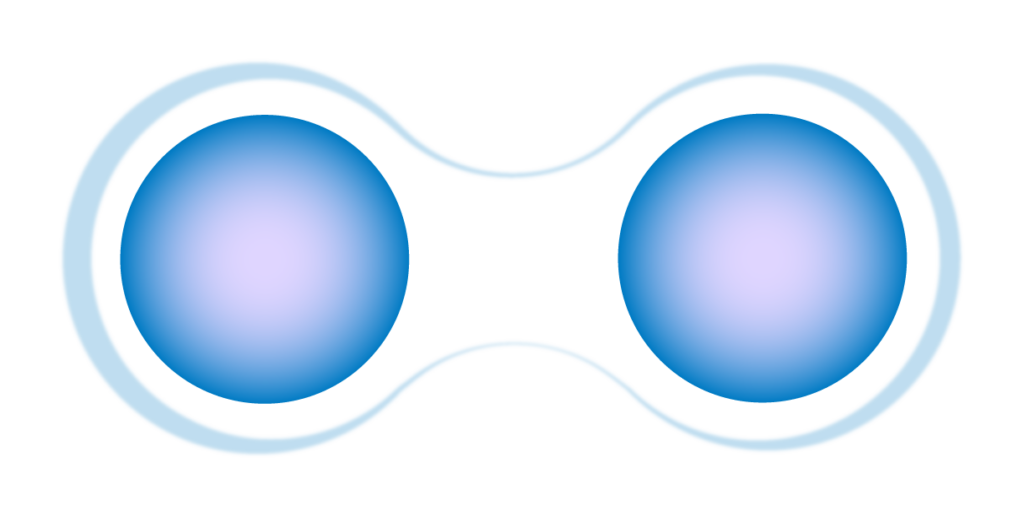
Quantum entanglement
In which two particles lose their individuality, so that the behavior of each one depends on the other regardless of the distance that separates them.
What are quantum technologies?
Quantum technologies are based on the principles of quantum physics, which studies matter and energy at its most fundamental level with the aim of discovering the properties and behaviors of the basic components of nature.
The quantum scenario opens up opportunities that were unforeseen until now. In general terms, there are two phenomena that feed these technologies to perform tasks more efficiently and to perform difficult or impossible calculations using classical technologies:
Quantum superposition
In which a particle can be in different states at the same time.

With more particles, the number of posibilities increases.
10 bits = 1 state of 10 bits each time
10 qubits = 1024 simultaneous states
Quantum entanglement
In which two particles lose their individuality, so that the behavior of each one depends on the other regardless of the distance that separates them.

How did Quantum Technologies evolve?
Early 20th Century
1st Quantum Revolution
Understanding the rules. Lead to the first disruptive technologies: Laser, Transistors, MRI, LED Screens…
Now
2nd Quantum Revolution
Development of tools. Disruptive technologies with transformative potential:
How did Quantum Technologies evolve?
Early 20th Century
1st Quantum Revolution
Understanding the rules. Lead to the first disruptive technologies: Laser, Transistors, MRI, LED Screens…
Now
2nd Quantum Revolution
Development of tools. Disruptive technologies with transformative potential:
Quantum computing
It allows solving unapproachable problems for classical computing and complex classical problems with exponentially higher efficiency. It has disruptive potential in areas as relevant as AI, drug design, personalized medicine or the chemical industry.

Quantum communication
It allows the transmission of quantum information, which guarantees the inviolability and privacy of communication. It is linked to the expectation of an ultra-secure internet: the quantum internet.

Quantum sensors
They are capable of detecting variations on a micro scale. This is why they allow the detection and measurement of elements with an unprecedented level of precision, such as the brain’s electrical signals or time (an example of a quantum sensor is the atomic clock).

Quantum computing
It allows solving unapproachable problems for classical computing and complex classical problems with exponentially higher efficiency. It has disruptive potential in areas as relevant as AI, drug design, personalized medicine or the chemical industry.

Quantum computing
It allows the transmission of quantum information, which guarantees the inviolability and privacy of communication. It is linked to the expectation of an ultra-secure internet: the quantum internet.

Quantum sensors
They are capable of detecting variations on a micro scale. This is why they allow the detection and measurement of elements with an unprecedented level of precision, such as the brain’s electrical signals or time (an example of a quantum sensor is the atomic clock).